How Does CBD Work?
The Biomolecules Types
Generations of people all over the world are using widely cannabis sativa or hemp for recreational and psychoactive intentions. Three types of biomolecules are present in cannabis:
- flavonoids
- terpenoids
- 60+ types of cannabinoids.
The pharmacological properties of this plant have taken a long time to be recognized.
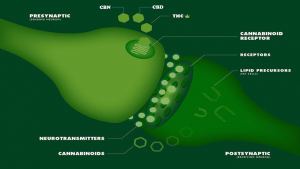
CB1 and CB2 receptors
All cannabinoids, including CBD, produce effects in the body by attaching to certain receptors. The human body produces certain cannabinoids on its own. It also has two receptors for cannabinoids, called the CB1 receptors and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are present throughout the body, but many are in the brain.
- THC binds directly to cell receptors to create a psychoactive response.
- CBD binds indirectly to cell receptors² to moderate signaling and the flow of other chemicals for a wide range of positive effects.
Phyto-cannabinoid is a family of natural complex chemicals found in cannabis. The most abundantly extracted phyto-cannabinoids from cannabis are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol).
While THC has a narrow therapeutic window, CBD has been identified for its analgesics, anti-inflammatory, and palliative properties (Turner, Williams, Iversen, & Whalley, 2017).
It is also inferred that the psychoactivity induced by THC is more adverse than its therapeutic effect. If the dosage is wrong identified, THC may become intolerable, ineffective and put the users in risk.
CBD, on the other hand, works as an allosteric modulator that reduces psychoactivity due to THC and follows an alternate pharmacological profile to inhibit cannabinoid receptors (Manzanares, Julian, & Carrascosa, 2006).
Inhaling THC and CBD, their bioavailability is higher than when ingested orally – they undergo extensive first-pass metabolism whereby lower doses of CBD are more therapeutic than THC. To understand the mechanism of action pursued by cannabinoids, it is important to explore the Endogeneous cannabinoid system (ECS) in the body.
ECS
ECS is responsible for neuromodulation, synaptic plasticity and the development of the central nervous system and peripheral system. It consists of enzymes, cannabinoid receptors such as
- CB1R (CNS-cannabinoid receptor)
- CB2R (peripheral cannabinoid receptor)
- TRP (Transient receptor potential)
- PPAR (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor)
and their ligands known as
- endogenous cannabinoids such as 2-AG ( 2-arachidonoyl glycerol)
- anandamide
- THC
- CBN(Cannabinol)
- CBD etc
CB1R are mostly found in the cortex, basal ganglia, hippocampus and cerebellum and they have critical roles in inducing muscle spasm, insomnia, chronic pain, and appetite stimulation.
Alternatively, CB2R are mostly found in immune system tissues, microglia, and vascular elements and they are responsible for inflammation. These receptors are not only located on the cell membrane but also expressed on intracellular organelles such as mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and nuclei.(Chakravarti, Ravi, & Ganju, 2014a)
Figure 1 illustrates how cannabinoid receptors interact with endocannabinoids to transmit retrograde synaptic messages.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.